Principles
The key components of Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment (CGA)
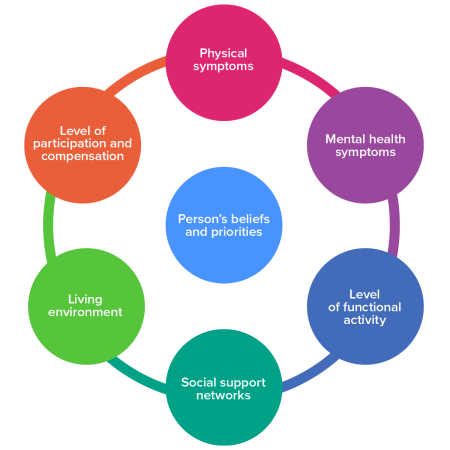
The gold standards for the management of frailty in older people is the process of care known as Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment (CGA). It involves a holistic, multidimensional, interdisciplinary assessment of an individual and has been demonstrated to be associated with improved outcomes.
- What is important to that person and their support network
- Self care
- Motivation to self manage
- Ability of carers or support network to cope or manage exacerbation/escalation of condition
- Co-morbid conditions and disease severity
- Pain / distress
- Medication review
- Nutritional status
- Problem list
- Pre existing mental health condition
- Depression and mood
- Anxiety and fear
- Delirium
- Cognition
- Relevant activities of daily living
- Gait and balance
- Activity / exercise status
- Falls History
- Informal support from family and friends
- Social network such as visitors or activities
- Eligibility for being offered care resources
- Voluntary support services / 3rd sector
- Home comfort, facilities, safety and finances
- Use or potential use of telehealth technology
- Transport facilities
- Access to local resources
- Neighbourhood team
- Home first principles
Back to Frailty pathways Back to Toolkit